Why Has The Treatment For Earwax Blockage Changed?

Why Has The Treatment For Earwax Blockage Changed?
Earwax is necessary for keeping dirt and bacteria out of our ears. On the other hand, excessive earwax can get lodged in the ear and cause earwax blockages. These problems might cause hearing loss and ear pain.
Throughout history, recommendations regarding the safety of various therapeutic procedures have developed. Understanding whether you are more likely to experience adverse side effects from earwax removal therapies is vital.
Earwax obstruction symptoms include:
Many people experience excessive earwax at some point in their life. Earwax is a natural substance that retains waste in the ear canals and falls typically out independently. On the other hand, excess earwax can build up in the ear and produce a blockage.
Earwax obstruction can cause a variety of unpleasant and uncomfortable symptoms, as well as more severe health issues. Hearing loss caused by earwax is a frequent symptom that, if left untreated, can have long-term consequences.
Any of the earwax blockage symptoms listed below may suggest a problem.
Earache.
The ear experiences a tingling feeling.
There is ringing or loudness in the ear (tinnitus).
Dizziness.

What Exactly Is Ear Irrigation?
This ancient ear injection and ear irrigation overlap; the former’s term is frequently used to represent the latter. However, the differences between the two approaches raise severe safety issues.
An electronic device that pumps low-pressure water into the ear, washing off the earwax, is used in the more contemporary type of ear irrigation.
Electronic irrigation is more controlled than hand spraying and thus safer.
It is common to eliminate earwax used by roughly 2 million people in England and Wales each year, either through the National Health Service or privately.
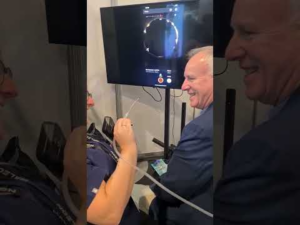
What Exactly Is Microsuction?
Microsuction is a dry earwax removal technique that uses a mild suction to remove earwax. Even though irrigation and micro-suction have minor risks, many experts believe micro-suction is slightly safer.
Certain groups of people are particularly exposed to the detrimental impacts of irrigation (although it is still considered a safe treatment for most people).
Microsuction has traditionally been given primarily in private health care settings, and it remains less generally available on the NHS than irrigation.
Side effects of micro-suction and irrigation
Both micro-suction and irrigation have the potential for several negative consequences.
These Are Some Examples:
The ear canal and tympanic membrane damage, including perforation
Ear canal and eardrum infection (otitis externa and otitis media).
Temporary deafness (or, in rare cases, permanent loss).
Tinnitus (a ringing in the ear).
Is Micro-Suction Less Dangerous Than Irrigation?
Both medicines have minor risks. However, micro-suction is less dangerous than irrigation. According to Peter Rea, the British Society of Otology president, some doctors have ceased using ear irrigation since more patients have experienced hearing loss symptoms after treatment.
In terms of safety, micro-suction has several advantages over-irrigation:
Medical practitioners utilise a microscope always to inspect the earwax, ear canal, and eardrum to see what they are doing.
Because micro-suction is performed without water, it is safe to perform even if you have an ear infection or a perforated eardrum.
Because there is little contact with the ear canal and eardrum skin, the danger of infection is significantly reduced.
The earwax removal tube comes in various sizes, making the method suited for small ear canals.
Who Might Be Affected By Irrigation?
It is critical to emphasise that recent research indicates that irrigation is safe and valuable for many people, with the advantages outweighing the negligible risk of harmful effects. On the other hand, specific groups of people should proceed with caution because they are at a higher risk of unfavourable side effects.
According to a 2020 study, people with weakened immune systems, diabetics, and the elderly are at higher risk.
NICE also advises avoiding using irrigation to remove earwax in anyone who has any of the following conditions:
The presence of ear illness (including a perforated eardrum, ear infection, and ear dermatitis).
Ear surgery, ear perforations, middle ear infections, or previous irrigation problems
A grommet is now in place. Small plastic tubes are known as “Grommets” are put into the eardrum following surgery.
In the preceding year, there was mucus flow from the ear.
A cleft palate, whether healed or not.
Hearing in only one ear if the treated ear is the one being treated.
Refusal to confirm or sit still (including young children and people with learning disabilities).
How standard are micro-suction and irrigation therapies?
According to NICE guidelines on managing excessive earwax, some people can now have earwax removed in their general practitioner’s office if it interferes with their hearing without being referred to a specialist facility.
On the other hand, Earwax removal is not one of the “core services” that primary care practises obligated to provide. Due to a shortage of trained staff, a significant percentage of practices do not provide this service.
Furthermore, individuals who have been told to avoid irrigation may have difficulty receiving microaspiration through the NHS, as availability varies by GP practice.